Benefits, Dosage, Interactions and Side Effects

[ad_1]
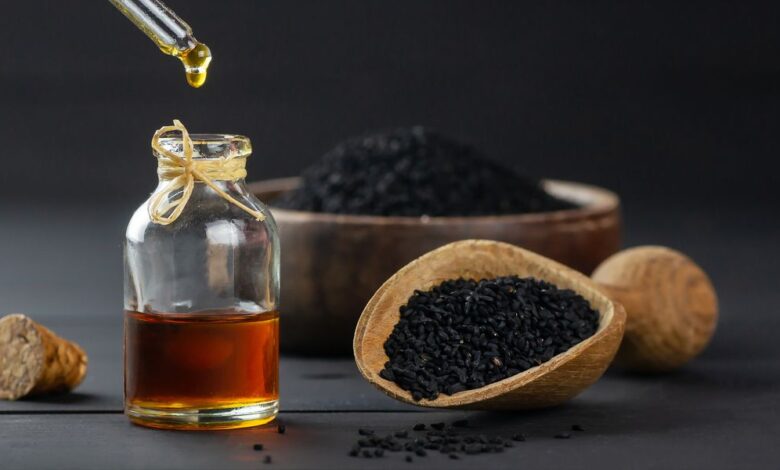
Used for thousands of years to treat various ailments, black seed oil has been touted for its proposed health benefits for centuries. Reports suggest it was even discovered in King Tut’s tomb. But are its health benefits legitimate? Here’s everything you need to know about black seed oil, including where it comes from and what to look for when purchasing it in supplement form.
This content is imported from {embed-name}. You may be able to find the same content in another format, or you may be able to find more information, at their web site.
What is black seed oil?
“Black seed oil comes from Nigella sativa, which is a small plant with pale purple, blue or white flowers that grows in Western Asia, Middle East and Eastern Europe,” says Kimberly Snyder, holistic wellness expert, New York Times bestselling author and founder of Solluna. She adds that alternative names for black seed oil include black caraway, black cumin, kalonji and black onion seeds. These tiny black seeds have been historically used in food preparation and cooking, but today are more commonly found in supplement form including capsules and soft gels.
Black seed oil health benefits:
Ancient medicine has attributed black seed oil to treating various ailments including headaches, toothaches, arthritis and several infections. “The Black Seed is a good source of essential amino acids, omega-3, omega-6, omega-9, Vitamin A (Retinoids) and super nutrients Nigellone and Thymoquinone, all of which boost the health of joints, skin and hair,” Snyder says. Some potential health benefits include that black seed oil:
- May help with blood pressure control: Findings from a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial suggest that consumption of 5 mL Nigella sativa oil daily for 8 weeks can lower both systolic and diastolic blood pressure in healthy individuals without any adverse effects.
- May reduce inflammation: “One animal study conducted at New York Medical College demonstrated that combining omega-3 fatty acids with a standardized oil from black cumin (Nigella sativa) may reduce inflammation caused by a high-fat (Western) diet,” Snyder explains. “Black seed oil has been shown to provide strong anti-pathogenic and anti-fungal properties in this review on the inhibitory potential of Nigella sativa.”
- May promote skin health: When applied topically, research revealed that black seed oil can decrease the severity of hand eczema and may be more effective than benzoyl peroxide in treating mild to moderate acne.
- May benefit individuals with asthma: A small randomized, double-controlled trial in asthmatic patients showed improved asthma control with black seed oil supplementation.
- May promote glycemic control: A review of both human and animal studies suggests that Nigella sativa may modulate hyperglycemia and improve glycemic status. When given with a hypoglycemic drug, one study found that black seed oil helped to reduce Hemoglobin A1C levels which measures average blood sugar over the course of three months.
- May assist with weight management: A systematic review suggests Nigella sativa supplementation may have a moderate effect on reduction in body weight, BMI and waist circumference, but the authors point out that limited high quality studies are available and more research is needed.
Potential black seed oil side effects:
“As is true with anything, there is potential for side effects while consuming black seed oil,” Snyder explains. “This is where your healthcare provider can advise on any potential side effects in relation to your diet and lifestyle, and any medications you may be taking while using this supplement.” She also adds that pregnant or breastfeeding women should speak with their doctor to see if black seed oil is right for them before using.
“Depending on the individual, when used topically, black seed oil may cause an allergic rash, therefore, it’s vital to test it on a small patch of skin first to ensure that it does not trigger a reaction.” Snyder says it’s important to keep the oil away from the eyes, nostrils and other sensitive body parts.
The 411 on black seed oil dosage:
If you get the green light from your healthcare practitioner, Snyder says that people typically can ingest black seed oil in the form of capsules or apply it topically to benefit skin health. “Personally, I sometimes add black seed oil into my massage oils and it’s also possible to add into shampoos and homemade skin-care products,” she shares.
Regarding dosage, Snyder says it is best to check with your healthcare provider on how much is best suited for your daily routine. “Choose 100% pure, therapeutic-grade, USDA-certified organic black seed oil” she recommends, like this option that she points out is USDA-Certified organic, high thymoquinone, 100% pure Nigella sativa, cold pressed, virgin and unrefined. “It’s important to note that the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not monitor herbs and supplements for quality and purity, so it is vital to be selective when purchasing these kinds of products and important to consult with your healthcare practitioner.”
Can you cook with black seed oil?
“In order to preserve the nutrients, it’s best to avoid heating black seed oil and it can be consumed raw. If you’re consuming black seed oil for the first time, it’s suggested you take one teaspoon at a time,” Snyder says.
She recommends mixing the recommended dose on the package with lemon juice or honey due to black seed oil’s strong taste. “Another way this oil can be added into your daily routine is to drizzle it on salads, add it into your afternoon smoothies or mix into your favorite tea, keeping in mind the caveat about its pungent taste.”
This content is created and maintained by a third party, and imported onto this page to help users provide their email addresses. You may be able to find more information about this and similar content at piano.io
[ad_2]
Source link