Bessemer’s 2021 cloud report provides context for soaring software startup valuations – TechCrunch
[ad_1]
Some well-known VC firms have spent the last few months crunching data while working to chart, graph, and map the world of venture investing. Happily for you and I, they’ve been pretty free with their time and data, helping us better understand today’s market for high-growth, software startups.
Last week The Exchange dug into data from Battery Ventures, which worked to explain some of the gains software companies have made in recent years in terms of their valuation multiples. The short gist is that multiples expansion — the repricing of software companies higher for each dollar of revenue they command — could be explained in part by segmenting the companies into various growth cohorts. Once accomplished, it’s easy to see that the fastest-growing software startups are enjoying the most price appreciation.
And as one Battery investor explained, growth rates de-risk valuation multiples.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money. Read it every morning on Extra Crunch, or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
The logic is sound enough. I can doodle on it in a future column if you’d like. But today, instead of retreading familiar ground, we’re diving into new data from Bessemer, a VC group that should be familiar to Exchange readers thanks to its cloud index that we refer to quite often. Regardless, Bessemer’s 2021 cloud report is out, and it assists some of the work we did with Battery’s charts.
What we can do with Bessemer’s dataset is extend the argument from Battery’s report: Sure, strong growth rates de-risk multiples, but what the new report indicates is that growth rates themselves amongst cloud companies (modern software, SaaS, call it what you will) should prove more durable than nearly anyone historically expected.
 You can quickly see the synthesis. If growth rates de-risk rising multiples, we can infer some logic to higher-growth companies being valued more richly than their slower-growing peers. But that doesn’t get us to understanding why multiples themselves might be rising, provided we wanted to find some argument for why they are sane. More durable growth rates, however, provide a possible answer.
You can quickly see the synthesis. If growth rates de-risk rising multiples, we can infer some logic to higher-growth companies being valued more richly than their slower-growing peers. But that doesn’t get us to understanding why multiples themselves might be rising, provided we wanted to find some argument for why they are sane. More durable growth rates, however, provide a possible answer.
Why? The longer a company can keep up its growth rate from year to year, the larger it will be in the future. Modern software companies do have a history of growth-rate-retardation over time, but nearly never negative growth rates.
More durable growth today implies more cash generation in the future. Up go valuations, and, for the fastest-growing today, the bump in worth comes with the valuation downside protection inherent in quick growth.
Got all that? If not, don’t worry — I have charts. Let’s keep going.
A theory for why software valuations aren’t irrational (maybe)
The key reason that startup and public-company software valuations are so high is because investors are willing to pay those prices. Hungry for yield on their capital, buying growth via software has been a trade for some time. It was even accelerated last summer as the pandemic gripped the global economy.
Suddenly software was not just a possible place to bet on growth, it was also a durable place to stash cash, because without software the world would stop. And that couldn’t happen, so most folks kept paying their software bills.
You might think that the valuation gains companies saw as other stocks fell out of favor would fade. After all, if they got a bump and the bump faded, surely they would lose some air from their balloon. Kinda? But mostly it appears that software valuations have stayed pretty damn aloft. And this brings us to the future.
Check out the following chart, via the Bessemer report (and shared with permission), that I will explain immediately afterwards:
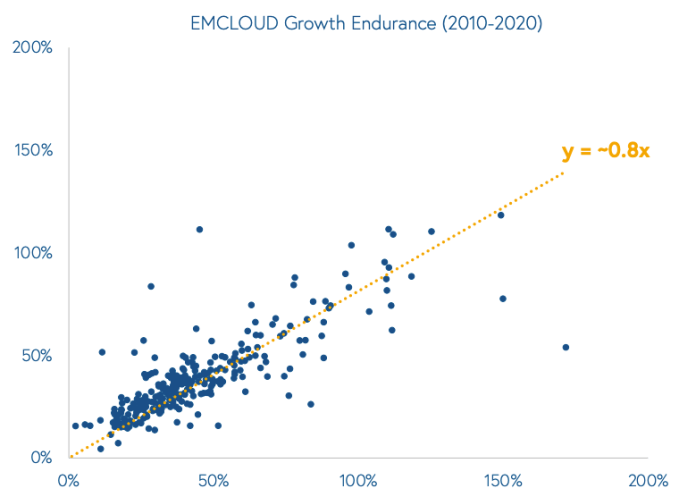
Bessemer partner Mary D’Onofrio, one of the report’s lead authors and part of the growth team, told us that the x-axis is a public software company’s last-year’s growth rate, while the y-axis is what it is managing in the current year. And that 0.8x? That’s the correlation.
[ad_2]
Source link






