Swarm’s low-cost satellite data network is now available to commercial clients – TechCrunch

[ad_1]
One of the original startups that set out to create a low-Earth orbit satellite constellation to provide a data network here on Earth is now open for business: Swarm, which now operates 81 of its sandwich-sized satellites on orbit, announced today that its network service is live and available to commercial customers.
Founded in 2017 by CEO Sara Spangelo and CTO Ben Longmier, Swarm has accomplished a lot in a relatively short time, culminating in its recent launch of 36 of its small satellites during SpaceX’s first ridesharing rocket launch late last month. Now that those are all online and operational, Swarm is able to provide full global network coverage, with the ability to check in with connected devices on its network up to multiple times per day.
Swarm’s offering uses embedded modems also designed and built by the company — the Swarm Tile, a tiny, low-powered modem that’s designed for maximum compatibility. The network is low-power and low-bandwidth, meaning it’s ideally suited for situations that require relatively low amounts of data transfer, but on a regular frequency over very long durations. That describes a wide range of use cases, including in shipping, logistics, agriculture and other Internet of Things (IoT ) deployments. The breadth of their customer base has actually been a surprise, and far outstripped the early vision for the startup.
“We actually started with the containership use case […] we talked a lot about how many containers there are in the world, how many ship there are in the world,” Spangelo told me in an interview. “We also knew that logistics, trucks and agriculture would probably be interesting markets. But I’m frankly surprised not only how many verticals this applies to — there’s a lot more in ag and global development and maritime than I probably ever anticipated — but also just the number of use cases within those industries.”
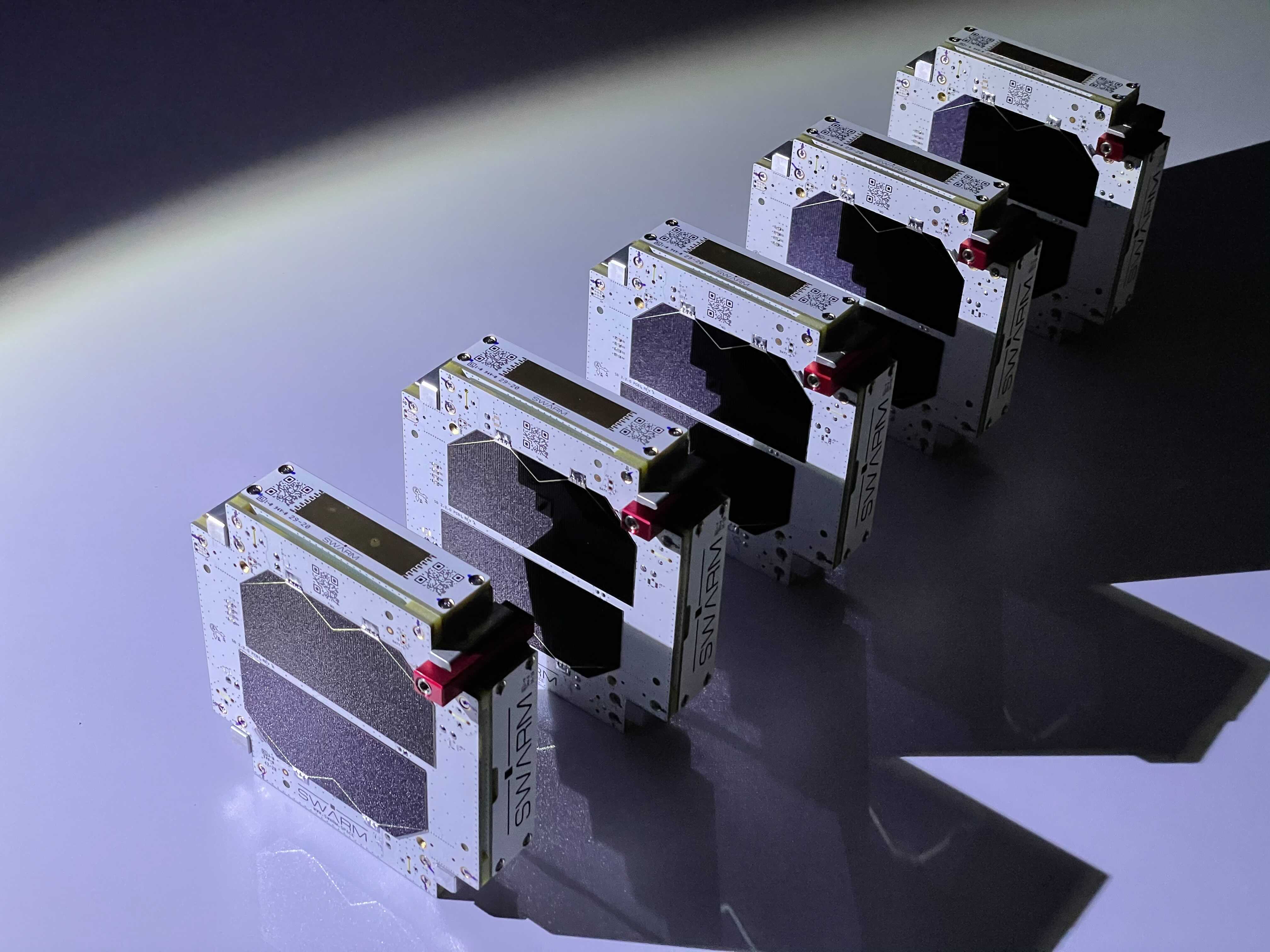
Swarm’s sandwich-sized IoT network satellites. Image Credits: Swarm
Spangelo is referring to the depth of the need for monitoring across the industries Swarm serves. So a client in green power wouldn’t want to just monitor the amount of power being generated by their turbines, but also to monitor the grid for power outgoing and power inbound. And in agriculture, industrial farms might want to monitor soil moisture levels, but also integrate Swarm connectivity in every single truck and tractor in operation in order to monitor their assets and their location. She also told me that vertically, she was surprised to discover just how many opportunities exist for low-bandwidth networks in construction, mining and defense.
Swarm’s focus at this stage is strictly commercial, but Spangelo said that people have even approached the company to see if they can purchase a Swarm Tile and use it with an app with their phone for providing basic emergency connectivity while hiking. She says “they’re not quite” at the point where they have a commercially available product for consumers, but it’s an idea they’re working on.
One key aspect of Swarm’s business model is affordability: Its service is available for just $5 per month per connected device (with a one-time cost of $119 for each Swarm Tile itself), which is far below any other satellite service available today. Spangelo says that has meant they are seeing new customers not only in the form of switchers from other satellite network providers, but also from businesses entirely new to satellite connectivity — and for some of those, it’s changing what’s possible at a fundamental level.
“Take wineries — it’s a high-yield type of crop,” she said. “People want to monitor very accurately the moisture and soil. Traditionally, they’ve only been able to do that within cell range. So think of like Sonoma and Napa, cell connectivity is actually really bad, because of the rolling hills. So now with Swarm you can have connectivity in those regions outside of cell, and provide that value, and much better knowledge and user data analytics to make much more informed business decisions, save water, save energy, save all those things.”
Some of these new use cases include projects like more finite weather and climate monitoring to try to assist with efforts to control and contain wildfires, as well as providing detailed tracking of the cold storage chain required to safely and effectively transport COVID-19 vaccines. Spangelo says this is one of the most exciting aspects of Swarm reaching this commercialization stage — seeing what new opportunities are possible that just couldn’t be done before.
[ad_2]
Source link






